The rapid evolution of electronic designs calls for precise decision-making on integrated circuit (IC) packaging. Land Grid Array (LGA) and Ball Grid Array (BGA) are two common packages, both with varied strengths and weaknesses that can significantly impact the performance, thermal regulation, and reliability of a device. The following article is purposed to give a thorough comparison of LGA and BGA to guide you to the best solution for your own applications.
What are LGA and BGA?
LGA and BGA are surface-mount technology packages that are designed to connect ICs to PCBs, ensuring reliable electrical contact while considering size, thermal performance, and mechanical integrity.
Land Grid Array (LGA)
An LGA package is formed of an array of conductive pads on the underside of the component. They contact corresponding pads on the PCB, typically kept in position using a mechanical socket. LGA is extensively applied for its potential to be reused and upgraded and therefore is an obvious choice where future upgrades are contemplated.

Ball Grid Array (BGA)
BGA utilizes solder balls in an array underneath the component as electrical and mechanical support. They suspend the component over the PCB during the soldering process. BGA's close-proximity connections make it suitable for high-performance applications in small sizes, such as smartphones' processors and graphics cards.
Key Differences Between LGA and BGA
Electrical Connection
LGA: Connection is made using flat pads which directly connect to the PCB, typically through a socket. LGA is hence extremely easy to take out and upgrade, making it superior where constant component swapping and upgrading are on the horizon.
BGA: Solder balls are utilized to form the electrical contacts as well as physically attach the component onto the PCB, thereby becoming more cumbersome to remove and replace after assembly.
Assembly and Repairability
LGA: More readily repairable and inspectable because of the socket-like design. Such ease in maintenance is crucial in settings where repair time may be costly.
BGA: BGA parts are difficult to repair because of the concealed solder balls and require specialized disassembly and assembly tools and expertise.
Size and Pin Density
LGA: Generally larger in dimension due to its contact pad architecture but supports higher pin counts demanded by complex systems.
BGA: Offers better pin density so more connections over a smaller surface, which is wanted in lower-sized systems like laptops and tablets.
Thermal Performance
LGA: Rides the heat away from the contact points that are metallic. Heat could be partially controlled by attaching extra heat sinks on the outside but thermal path falls behind BGA.
BGA: The solder balls are effective thermal paths, which themselves tend to result in better thermal control, especially for high-power applications where effective heat dissipation is critical.
Cost and Production
LGA: Less expensive overall with fewer steps in the manufacturing process; however, complex designs will increase cost. Its ease of reworkability can also reduce long-term costs through applications involving frequent upgrading or maintenance.
BGA: Higher initial manufacturing cost can be offset by the long-term benefits of high-density and performance-oriented applications.
Applications and Use Cases
Understanding the strengths of each technology assists in making an informed decision.
LGA Applications:
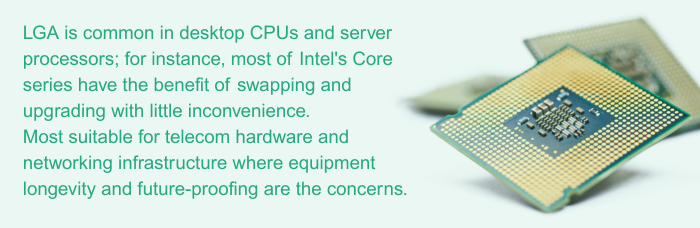
Common in desktop CPUs and server processors, for instance, most of Intel's Core series, which have the benefit of swapping and upgrading with little inconvenience.
Most suitable for telecom hardware and networking infrastructure where equipment longevity and future-proofing are the concerns.
Used in applications like data centers where server replacements are frequent, so reworkability is a benefit.
BGA Applications:
Perfect for portable and mobile applications that need to occupy little space, like smartphones, tablets, and gaming systems.
Perfect for high-frequency, performance-driven applications like graphics processing units and automobile control units.
Typically used in consumer electronics and telecommunication equipment that require efficient thermal management and low footprint.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between LGA and BGA
Pin Count: BGA best suits designs with a need for many connections. If area issues are less problematic, the LGA capability of more pins would be desirable.
Thermal Management: BGA typically has better thermal management capabilities, important when high power or high-frequency are involved.
Repairability and Inspection: LGA parts are less difficult to diagnose and fix, which could be essential to ensure minimal system down time.
Budget Restraints: Both short- and long-term cost are accounted for; initial cost savings with LGA are offset by BGA's strengths in high-density designs.
Space and Floor Planning: Small size of BGA is advantageous to designs with extreme space constraints.
Mechanical Stability: LGA has the potential to provide more mechanical support, which is useful in applications with high mechanical stress.
Request for High-Complexity PCB Assemby Quote
In summary, whether to use Land Grid Array (LGA) or Ball Grid Array (BGA) packaging is quite crucial and must be directed by the specific needs of your electronic design project. LGA is useful for ease in fixing and cost saving and is ideal in scenarios where much swapping of components would be happening. But BGA excels in scenarios with high levels of performance that entail little available space and maximum heat management. By understanding the specific strengths and weaknesses of each technology, you can make an informed decision that best fits the performance, reliability, and thermal needs of your devices.
Choosing the right partner for PCB fabrication and assembly can also boost the success of your electronics projects. PCBCart is a good choice, with state-of-the-art manufacturing and quality control to cater to your needs efficiently. Committed to precision and customer satisfaction, PCBCart can help you turn your designs into high-performance products. Request a quote today and find out how PCBCart can help your next innovation give the highest level of functionality and longevity to your electronic products.
Helpful resources:
• A Guide to Ball Grid Arrays
• BGA Assembly Capability
• Comparison between Ultra Fine Pitch QFP and BGA and Their Development Trend
• An Introduction to BGA Package
• QFN vs. QFP Packages: Choosing the Right IC for Your PCB














