In the world of sophisticated electronics, printed circuit boards (PCBs) and printed circuit board assemblies (PCBAs) are key figures representing different stages of the process of making electronics. Although used interchangeably, they refer to different aspects essential for the operation and assembly of electronic products. Being a content expert with PCBCart, one of the leading providers of PCB solutions, this article attempts to describe the differences succinctly and professionally and offer valuable information for electronics designers, manufacturers, or repair technicians.
Defining PCB: The Cornerstone of Electronics
A printed circuit board (PCB) is the fundamental base of nearly every electronic device, providing a platform that mechanically supports and electrically connects electronic components.
Key Features of PCBs
Structure and Materials: PCBs are constructed out of laminate materials such as composite epoxy or fiberglass. They consist of conductive copper paths etched on a substrate that gives them good mechanical and electrical connections in the circuit plan.
Types of PCBs:
Single-layer PCBs: They have a single layer of conducting material and are the easiest type, with a silkscreen for easy identification of components.
Double-layer PCBs: These include conductive material on two sides of the board that are more flexible and compact compared to single-layer PCBs.
Multi-layer PCBs: With over two layers of conductive material, these are used in high-complexity applications with sophisticated circuitry.
Specialty PCBs: Flexible, rigid, and rigid-flex versions that cater to specific industrial needs and environments.
Applications: PCBs are employed in a vast array of devices, ranging from computers, cell phones, and televisions to automobile electronics and advanced medical equipment like pacemakers and imaging devices.
Manufacturing Process of PCBs
The manufacture of a PCB is a process in several stages:
Design: Engineers utilize CAD software to develop schematic layouts for the PCB, determining electrical connectivity and component location necessary for the subsequent steps.
Layering and Etching: Conductive lines are etched on the substrate according to the requirement of the design. Multi-layer boards undergo additional processing to align and connect each layer properly.
Drilling and Plating: Holes are drilled at specific locations for component leads and vias, and plated to ensure good electrical connections.
Surface Finishing: Different finishes, such as HASL, ENIG, or OSP, are deposited to insulate copper lines and assist in soldering.
Quality Assurance: All PCBs are thoroughly tested to validate their structural integrity and adherence to design specifications.
Defining PCBA: The Functional Assembly
A printed circuit board assembly (PCBA) refers to an assembly of electronic elements onto a PCB that transforms it into a functional circuit that is capable of performing its intended function. This transformation is through advanced assembly techniques that ensure component accuracy and reliability.
Assembly techniques in PCBA Manufacturing
Surface-Mount Technology (SMT): SMT involves the mounting of components onto the surface of the PCB such that there are denser concentrations of connections and less bulky board sizes.
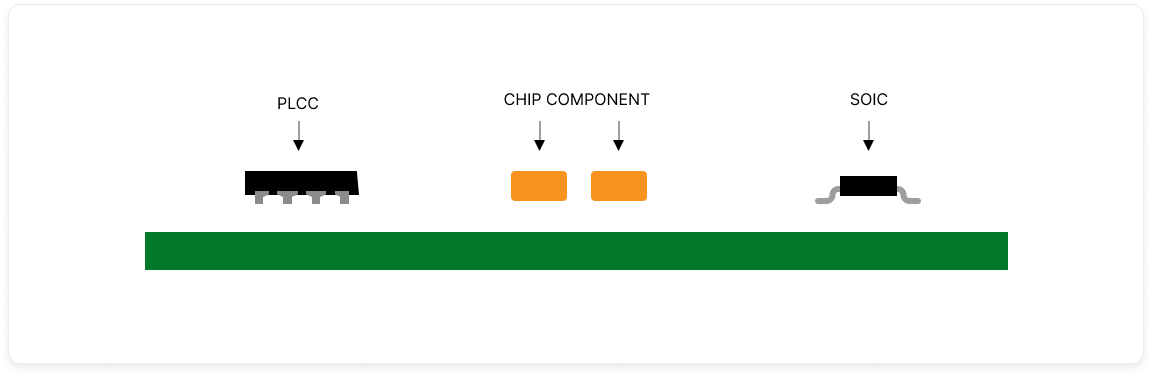
Process Steps:
Solder Paste Staging: Solder paste is applied on the regions of the PCB where components are to be installed.
Component Placement: Automatic equipment places components onto solder paste with high precision.
Reflow Soldering: The board is subjected to heat in a reflow oven, which melts the solder paste to form solid electrical connections.
Inspection: Manual checks and optical inspections verify proper placement and functionality.
Thru-Hole Technology: Component leads are inserted into holes drilled ahead of time, providing robust mechanical bonds for physically stressed components.
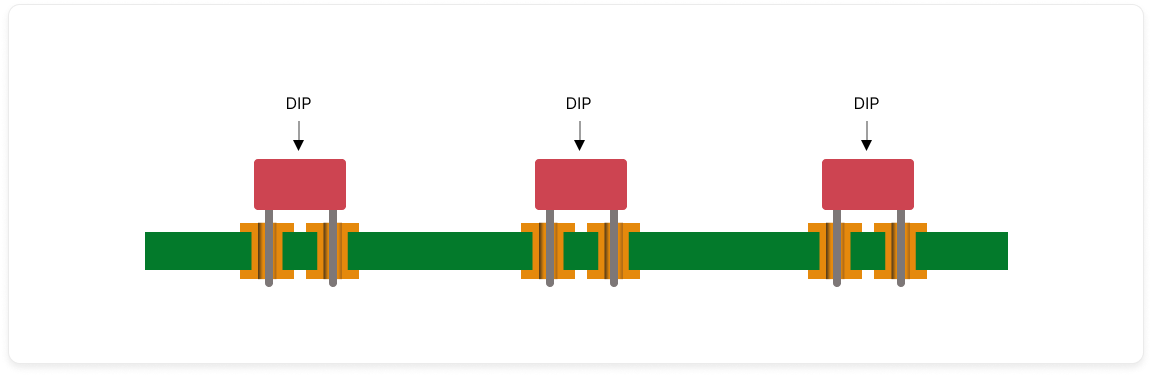
Procedure:
Drilling: Holes are drilled to accommodate the component leads.
Insertion of Leads: Carefully, component leads are inserted through the holes.
Soldering: Solder is applied to secure the leads.
Inspection: Total inspections ensure the quality and performance of the assembly.
Interrelationship Between PCB and PCBA
The interrelation between PCBs and PCBAs is elementary but core. A PCB is a base—a bare board of which components will be mounted on. On the contrary, a PCBA is the final product of this process, wherein components are mounted to become a functional electronic component.
Key Differences:
Functionality: PCBs are bare structures waiting to be functional, while PCBAs are complete assemblies waiting to function in electronic devices.
Production Stage: Production of PCB incorporates substrate and trace preparation, while PCBA entails component assembly and soldering with more complexity and need for quality control.
Cost and Difficulty: The process of manufacturing a PCB is typically less costly and involved than the process of putting together a PCBA, i.e., buying and precise insertion of components, testing.
Packaging: PCBs are generally vacuum-packaged to keep it free from contamination, while PCBAs are packaged in anti-static or compartmental packaging to protect delicate components.
In summary, understanding the difference between PCBs and PCBAs is utmost for everyone in the electronics business. PCBs, as building blocks, provide electronic devices with the physical and electrical framework required. They are constructed from durable materials and serve as the plain canvases on which circuits are built. PCBAs, however, transform such plain canvases into working, ready-to-use units by adding the electronic components needed to the PCBs. The assembly operations—both Surface-Mount Technology (SMT) and Thru-Hole Technology—are enhancing the precision and reliability of the electronic assemblies so that PCBAs become a critical component of the functionality of devices in different industries. Recognizing these distinctions not only enhances manufacturing effectiveness but also enables the making of reliable, high-quality electronics.
PCBCart is your industrial leading company as a reliable partner of all your requirements in PCB and PCBA. With focus on precision, accuracy, and customer satisfaction, we offer tailored solutions to meet diverse manufacturing requirements. Our cutting-edge infrastructure and experienced team of professionals ensure strict quality control at all stages of production, from the initial stages of PCB designing to the complex assembly of PCBAs. Whether from the market for pilot runs or bulk orders, our expertise ensures top-notch results. We invite you to visit our website for further detailed information and to get an instant quote—you'll discover how PCBCart can help realize your electronic projects effectively and efficiently.







