PCB side plating is the metallization of the edge or side of a PCB. It is the thin layer of copper deposited from the top surface to the bottom surface and along the sides, which improves electrical conductivity as well as mechanical strength. The most common surface finishes employed for side plating include Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold (ENIG), Electroless Nickel Electroless Palladium Immersion Gold (ENEPIG), and Hot Air Solder Leveling (HASL), among others. These treatments help improve electrical connectivity and protect the plated areas from oxidation and corrosion.
The Benefits of PCB Side Plating
Enhanced Electrical Connectivity
Side plating is responsible for forming continuous electrical paths across different PCB layers—a highly desirable feature for applications that require high signal integrity. It enhances the performance of high-frequency signals, and side plating becomes necessary in RF and microwave applications where the quality of signals has to be preserved at any cost.
Better Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)
By wrapping the PCB in a Faraday cage, side plating suppresses electromagnetic emissions and protects sensitive internal circuits from external interference. This not only aids EMC compliance but also protects the board's operation within high electromagnetic interference (EMI) environments.
Enhanced Mechanical Strength
Edge metallization provides excellent mechanical support and makes the PCBs stronger against lateral forces as well as mechanical stress. Extra strength is most crucial for boards applied to applications involving repetitive handling, vibration, or stringent operating conditions.
Better Thermal Management
Side plating provides a back-up conductive path to facilitate better heat dissipation. This is particularly useful in the case of high-power applications because it keeps the internal temperature within the safety range, thus extending the life of the PCB.
Innovative Design Solutions
The flexibility fostered by side plating facilitates innovative design solutions, such as constructing secondary contacts using edge pads and improving general assembly quality by implementing superior soldering techniques.
Environmental Protection
The addition of a metallized edge offers protection from environmental issues like moisture and corrosive chemicals, valuable for deployment in extreme environments or where long-term exposure would otherwise result in degradation.
PCB Side Plating Applications
Side plating exists in numerous applications where reliability and high performance are critical:
Communication Modules:
Wi-Fi and Bluetooth modules tend to have side plating to offer stable and efficient connection, which is crucial for the prevention of equipment failure.
RF and Microwave Devices:
Signal integrity is of critical concern in high-frequency electronic devices, and side plating is a precious technique to minimize interference and enhance overall performance.
Consumer Electronics:
Compact consumer devices such as smartphones and wearables benefit from the double advantage of space savings and enhanced functionality through side plating.
Industrial and Automotive Electronics:
Where mechanical stress or harsh environment exposure comes into play, side plating provides the necessary durability and protection.
Implementing Side Plating in PCB Designing
Side plating in PCB designing is done by following intricate planning and the guidelines to make it functional as well as manufacturable:
Defining Copper Overlap:
In the CAD setup, copper overlap (surfaces, pads, or tracks) needs to be defined to establish the metalized regions. Ensure a minimum of 500 μm overlap, with a minimum of 300 μm for connection layers. Ensure at least 800 μm separation on non-connection layers from the edge to avoid spurious connections.

Ground Plane Connections:
Precise ground plane connection in all the layers, even internal ones, enhances shielding effectiveness and overall electrical performance.
Clearance and Restrictions:
Design a minimum 10 mils clearance between edge plating and other copper details, and cross-reference manufacturers to set a mutual value. Avoid placing vias near edges to prevent any problems; if there's a requirement, consult your contract manufacturer.
Consideration for Edge-Mounted Components:
Avoid edge plating from encroaching on edge-mounted connectors like SMA. Create cutouts for these components in the plating.
Castellated Holes:
If castellated holes are part of the design, ensure that the edge plating wraps around such holes to provide good solder points.
Thermal Considerations:
In thermal management with side plating, connect it to inner ground planes via thermal vias to provide strength to heat dissipation.
High-Frequency and RF Designs:
For these designs, consider the impact of side plating on controlled impedance traces close to the edge of the board. Trace widths might have to be changed or extra clearance from the edge.
Mechanical Connection Points:
Place anchor strips along the edges to serve as mechanical connection points to firmly hold the side plate onto the PCB.
Manufacturing Process of Side Plating
The manufacturing process is a cautious one to effectively put in place effective plating:
Edge Preparation:
Board edges are cleaned, degreased, roughened, and precision-milled to achieve the optimum plating adhesion.
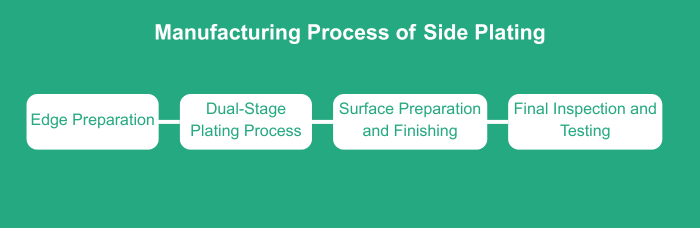
Dual-Stage Plating Process:
A thin layer of copper is initially deposited through electroless plating and a thicker layer through electrolytic plating to achieve the desired thickness.
Surface Preparation and Finishing:
The excess copper is etched out, and other finishes like ENIG are deposited to increase corrosion resistance and solderability.
Final Inspection and Testing:
Close inspection ensures compliance with thickness, continuity, and adhesion requirements, with defects repaired before final test and assembly.
Side-plated PCB production has some constraints, such as that continuous plating of the entire edge is not feasible due to manufacturing panel fixturing requirements. Side-plated edge V-cutting scores should be avoided in design layouts, and adequate routing layout allowance must be provided before through-hole plating starts.
PCB side plating is a significant advance in PCB technology that offers unmatched excellence in electrical and mechanical performance, thermal conductivity, and environmental insulation. As there are higher demands for electronic products with improved performance, strategically applied side plating will be at the core of meeting the requirements, with greater functionality, and reliability for diverse applications. Through adhering to design and manufacturing best practices, engineers are able to take full advantage of PCB side plating's capability to deliver improved electronic solutions.
PCBCart is your ideal partner for deploying advanced PCB capabilities like side plating. Through our modern manufacturing facilities and highly skilled team of professionals, we deliver exceptional quality and accuracy in every PCB project. Our commitment to innovation and customer satisfaction ensures your designs come to life to the highest level of quality, however complex. Be a part of the PCBCart difference by obtaining a quote today. We want to assist you in bringing your design ideas to life through unparalleled service and expertise.
Request for PCB Assembly & PCB Manufacturing Quote
Helpful Resources
• How Much Do You Know About Flying Probe Test for PCB and PCBA?
• Lead-Free Solutions for Custom PCB Services | PCBCart
• Blind Via and Buried Via PCB
• PCB Layer Stackup, PCB Stackup Design | PCBCart
• PCB Manufacturing Process — A Step-by-Step Guide
• Via In Pad PCB Technology | PCBCart














