In the fast-changing world of PCB manufacturing, compliance with environmental regulations has become indispensable to achieving global competitiveness. Central to this evolution is the adoption of lead-free processes, mainly driven by the RoHS directive. This transition satisfies the legal mandate but also encourages eco-friendly and sustainable manufacturing practices. The article delves into lead-free HASL, its synergy with RoHS standards, and a discussion on temperature issues in its implementation faced by manufacturers.

Importance of Lead-Free HASL
HASL has remained a popular choice because of its cost efficiency and reliable solderability. Conventional HASL included the use of a tin-lead solder alloy, which gave a smooth, even coat over the copper pads. However, due to increased environmental controls and their stringency, the industry is already moving toward lead-free HASL with various other alloys like Sn-Ag-Cu and Sn-Cu.
Switching to lead-free HASL is significant because of the great health and environmental risks caused by lead exposure. Adopting lead-free HASL helps the manufacturers reduce these risks and work towards global sustainability objectives. Besides that, lead-free HASL provides a rugged surface finish with assured solderability of surface-mount and through-hole components, essential for complicated PCBs when they go through several stages of soldering.
Understanding RoHS Compliance
The RoHS directive of the European Union, enforced since 2006, prohibits the use of six hazardous substances such as lead in electronic and electrical equipment. Therefore, to be compliant, the lead content on PCBs should be less than 0.1% of the total weight in homogeneous materials. This enforcement has pushed the industry towards lead-free options like HASL. Non-compliance would therefore limit market access, with substantial financial and reputational damages, particularly for companies exporting to areas with rigorous environmental standards.
Achieving RoHS compliance goes beyond penalty avoidance; it addresses increasing consumer demand for eco-friendly products across sectors such as automotive, consumer electronics, and telecommunications. By leveraging lead-free HASL, producers reach legal compliance and boost their product appeal and trust among consumers.
Mastering the Lead-Free HASL Process: Temperature Considerations
Transition to lead-free HASL includes several changes to accommodate the higher melting point of new alloys relative to traditional tin-lead solders. The following key steps are included in the process:
Cleaning: This stage involves removing contaminants from PCB surfaces to achieve good solder adhesion.
Flux Application: Apply a flux layer to prevent oxidation and enhance solder wetting.
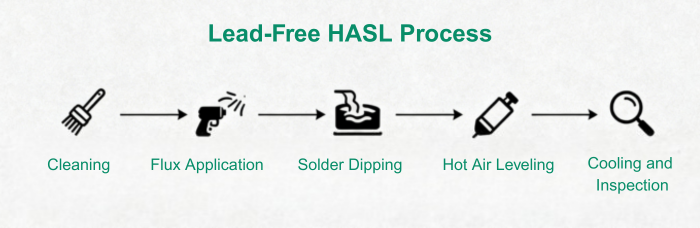
Solder Dipping: Dip the board into molten lead-free solder.
Hot Air Leveling: Hot air knives are used to evenly distribute solder over the surface.
Cooling and Inspection: Let the board cool down, then inspect for defects and uniformity.
Another important difference from lead-free HASL is the higher temperature requirement. The melting point of conventional tin-lead solder is around 183°C, while for lead-free alloys like Sn-Ag-Cu, it may be well over 217°C. The equipment and reflow profiles must therefore be cautiously optimized by manufacturers to manage thermal stress and avoid damage to either the PCB substrate or components.
Lead-Free Solder Alloys Investigations
Selecting the right solder alloy is important for successful lead-free HASL implementation. Common lead-free alloys include:
Sn-Ag-Cu (SAC): Recognized for its mechanical robustness and thermal reliability, thus being widely used in high-performance applications.
Sn-Cu: Because this alloy is silver-free, it is less expensive. It has somewhat lower mechanical and thermal capacities than SAC alloys.
Sn-Bi: Tin-Bismuth has a lowered melting temperature and hence is suitable for temperature-sensitive components. The use of Sn-Bi in HASL is less common due to its brittleness.
These alloys form strong solder bonds necessary for the modern methods of assembly, but their higher melting points require careful management of a thermal profile to prevent component harm.
HASL Alternatives Review
While lead-free HASL is prolific, other options exist for RoHS compliance with their own particular advantages:
ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold): Provides excellent corrosion resistance and flatness, ideal for fine-pitch components; however, it is more expensive.
OSP (Organic Solderability Preservative): Cost-effective option, though only suitable for simpler boards and not for repeated cycles.
Immersion Tin and Silver: Provide smooth, conductive surfaces. Immersion Tin tends to cause whisker growth, while Immersion Silver, although it tarnishes after some time, serves well in high-frequency applications.
The choice depends on various specific project needs such as budget, component density, and environmental conditions.
Best Practices for Lead-Free HASL
The following best practices will help to take full advantage of the functionality of lead-free HASL:
Material Selection: Select materials and components that can tolerate the higher temperatures of lead-free soldering.
Process Control: Maintain stringent control of soldering process variables for better repeatability with minimal defects.
Storage Management: Protect finalized boards from oxidation through controlled storage, which extends shelf life and maintains solderability.
Quality Assurance: Utilize comprehensive testing processes, such as solderability tests and thermal stress tests, to verify the quality and compliance of the products.

Advancing Sustainable Manufacturing Transitioning to lead-free HASL involves regulatory compliance and sustainable production. By learning about the processes of lead-free HASL and managing temperature challenges associated with these processes, a manufacturer is able to provide high-quality, environmentally sensitive products that meet the demands of today's markets. As regulations continue to evolve, embracing a lead-free practice is not only called for but represents a critical point of opportunity in innovating electronics. Whether for consumer electronics or automotive systems, lead-free HASL is indispensable to balancing technical excellence with environmental responsibility.
At PCBCart, we're leading the way in this transition with our sophisticated PCB manufacturing solutions for lead-free HASL processes. With our expertise in handling complex projects that are sensitive to temperature in soldering, we can ensure that every project meets high standards of quality and compliance. Partnering with PCBCart ties in technical precision with environmental responsibility. Request a quote with PCBCart today, and let's see how our customized services can further your PCB manufacturing projects in compliance with regulatory and environmental policies.
Helpful Resources
• PCB Manufacturing Process — A Step-by-Step Guide
• How to Prevent Poor Solder Wetting
• PCB Surface Finishes Introduction and Comparison
• How to Ensure the Quality of PCBs
• Contrast on Soldering Technologies Used in Lead and Lead-Free Reflow Soldering







