Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are integral parts of modern electronics, both as the mechanical support and as the electrical paths needed for the function of various devices. PCBCart provides high-quality PCB solutions to ensure that your electronics projects function optimally. This in-depth guide explores the basics of PCB design, the critical components of PCBs, and the significance of their design and assembly.
Introduction to PCBs
PCBs are consumer products' workhorses, industrial devices' workhorses, telecommunication products' workhorses, and many others. They physically support and electrically connect electronic components through conductive tracks and pads typically made of etched copper, attached to a non-conductive base like fiberglass or epoxy resin. The substrate provides the structural rigidity in order to prevent breakage such as bending and snapping.
Types of PCBs
The PCBs are grouped primarily according to the quantity of copper layers present in them:
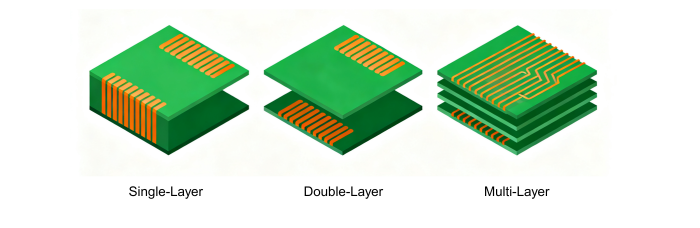
Single-layer (Single-sided) PCBs: They contain a single copper conductive layer and are employed in simple electronic devices due to their simplicity and cheapness in designing. They can be applied in low-density designs, such as hobby projects and simple electronic devices.
Double-layer (Double-sided) PCBs: With copper layers on top and bottom of a single substrate, double-layered PCBs allow for more complex circuits than single-layered PCBs. Components can route through either side, with more routing flexibility without having to lose the relatively simple structure.
Multi-layer PCBs: These PCBs consist of many layers of copper with insulating material sandwiched between each layer. Through vias (vertical interconnect access) are used to connect the layers, enabling more intricate circuit designs. These PCBs are necessary to house high-power and complex applications, such as advanced computers and telecommunications equipment, as they provide the ability to support more intricate routing and component placement.
Composition of a PCB
A PCB is made up of several layers, which all help in its making and functioning:
Substrate (Base Material): The foundation of a PCB, typically built from FR-4, a glass-reinforced epoxy laminate. The material provides the necessary stiffness and fire resistance. In flexible applications, PCBs use flexible plastic substrates, while metal-core (typically aluminum) PCBs are employed in those applications requiring improved heat spreading.
Copper Layer: PCB's lifeline, copper allows for creating electrical connections. Copper thickness is important and usually quoted in ounces per square foot. A majority of boards have one-ounce copper, capable of handling most electronic loads of current, but high power circuits could require heavier copper.
Solder Mask: Applied on top of the copper layer, it is a lacquer-type coating that protects copper traces from unintended metal contact, solder bridges, or conductive residue. Green is common, but solder masks are available in other colors to suit various needs or preferences.
Silkscreen: This topmost layer prints symbols, numbers, and letters onto the board to present needed information at hand for easy assembly and maintenance. The silkscreen typically uses white ink for readability, displaying component values, part numbers, and other significant identifiers.
Major Components on a PCB
Each component soldered onto a PCB plays a very crucial role in causing the board to perform its specific function. Some of the most common components found on PCBs include:
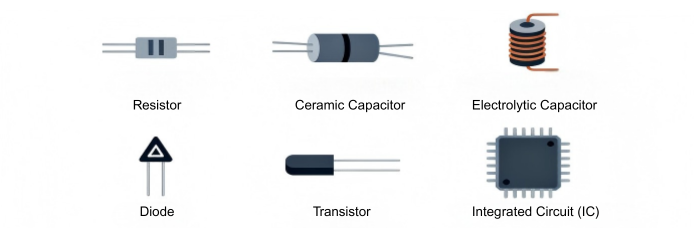
Resistors: Resistors are fundamentals for voltage dividing and voltage controlling, and they control the flow of current through the circuit. Their value is a critical aspect of circuit design in ohms and is crucial to controlling current in the system.
Capacitors: Capacitors are energy storage devices that can quickly charge and release electric energy, filtering and regulating voltage and power transmission. They are crucial to use in filtering and power supply systems.
Inductors: Primarily applied in power supplies and filtering, inductors are energy storage devices in a magnetic field as current flows through them. Inductors resist changes in current and are employed as AC circuit chokes.
Diodes: Allow current to flow in only one direction, providing direction conductivity. This characteristic makes them essential in rectification and protection of circuits from reverse voltage damage.
Transistors: Crucial for amplifying signals or switching electrical power, transistors control the passage of electricity within a circuit. They form the core of digital circuits and logic gates.
Integrated Circuits (ICs): As versatile electronic circuits, ICs are able to perform a wide variety of functions, ranging from simple logic operations to advanced processing in microcontrollers and CPUs.
Connectors: Facilitate interconnecting different PCBs or external devices, allowing seamless incorporation in broader electronic systems.
The Importances of PCB Assembly
How PCBs are assembled makes a great difference in their performance and reliability. Multi-layer boards pose special design and manufacturing difficulties but enable more sophisticated circuit designs that single and double-layer boards cannot accommodate.
Component Mounting Methods also become a significant factor:
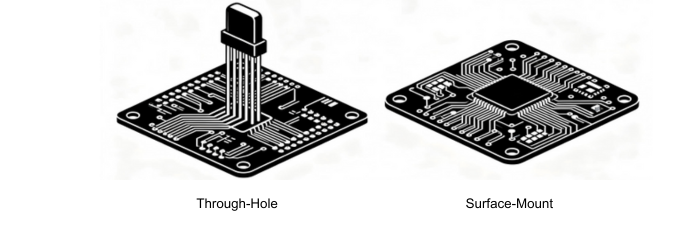
Through-hole Technology: Components are mounted through holes and soldered on the back side. This method is very robust, the best for components under mechanical stress.
Surface Mount Technology (SMT): Chips are mounted on the surface of the PCB, making it possible to fit smaller chips and more components into a given smaller space. The process is required for present-day, miniaturized electronics and equipment with high circuit complexity requirements.
Understanding the specifics of the PCB design, such as the type of board, components used, and their assembly, is the secret to creating effective and functional electronic devices. Here at PCBCart, our specialty is providing custom PCB solutions to ensure your design and product achieve the intended functionality with precision. From simple to intricate multi-layered circuits, our services allow for the development of new technology. Contact us today and discover how we can help your next electronics project with our expert PCB manufacturing and design solutions.
Request for High-quality PCB Assembly & Fabrication Quote Now
Helpful resources:
• Printed Circuit Board Terminology
• PCB Manufacturing Process — A Step-by-Step Guide
• PCB Materials
• Free DFM Check
• Common PCB Issues and Repairs
• How to Choose the Right PCB Assembly Services?






