In the competitive world of printed circuit board (PCB) manufacturing, surface finishes are critical in order to ensure good-quality boards. Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold (ENIG) surface finish is in high demand because it provides excellent corrosion resistance and solderability properties. However, in order to ensure high-quality ENIG surface finish, there are certain parameters that must be followed; specifically, the IPC 4552 standard must be observed.
The Importance of IPC Standards in PCB Manufacturing
IPC standards act as global practice guidelines that promote quality and reliability in electronic product manufacturing. Based on ENIG finishes, the most important IPC standard is the IPC-4552 standard. This standard provides information on the process and conditions that the finish has to meet to resist the effects of the various solders and environmental conditions.

Following the standards outlined by the IPC is necessary for many reasons:
Reliability: Even with compliance to IPC, sometimes there could be a slight failure of reliability due to non-standard finishing.
Defect Prevention: Standards can prevent problems such as nickel corrosion or "black pad," failures because of which solder joints can go wrong.
Trust Building: It shows commitment to quality, and this instills trust among clients and business partners.
IPC-4552: What Makes Great ENIG Finish Quality
The IPC-4552 standard, which has been upgraded to IPC-4552B since its introduction in the year 2002, deals with some of the emerging issues in the PCB manufacturing domain. This includes key parameters in ENIG plating.
One of the major aspects of IPC-4552B is the emphasis on the suppression of nickel corrosion. Earlier ranges were focused on thickness, but the current revision has laid down proper procedures for the evaluation and suppression of corrosion, which assumes utmost importance in the field of high reliability, such as aerospace and biomedical equipment. Moreover, the present standard, IPC-4552, helps ranges to develop a procedure for the validation of the ENIG process.
Core Requirements of the ENIG IPC-4552
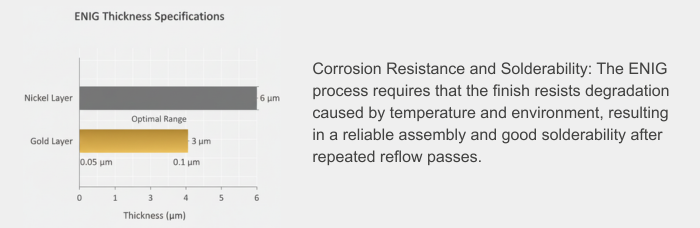
Nickel Layer Thickness: Given a range between 3 and 6 micrometers (µm), which is adequate enough to provide a protective coating against corrosion.
Thickness of Gold Layer: Thickness should be between 0.05 µm to 0.1 µm. This is with regard to cost consideration as well as effectiveness. Nickel corrosion can be increased with thickness beyond 0.125 µm.
Corrosion Resistance and Solderability: The ENIG process requires that the finish resists degradation caused by temperature and environment, resulting in a reliable assembly and good solderability after repeated reflow passes.
Ensuring High-Quality ENIG Plating
The quality of the plating is one of the most important factors which can affect the performance and life span of the PCB.
Process Consistency: The consistency of bath chemistry, temperatures, and immersion times to prevent defects.
Purity of Materials: Purity of the chemical used leads to an absence of contamination that may affect the finish.
Corrosion Prevention: A minimized porosity of the gold layer prevents oxidation of nickel.
Balancing ENIG Thickness Specifications
Adherence to the thickness specification is imperative. The thickness of the nickel layer, acting as a barrier, must fall between 3 to 6 µm for proper diffusion and protection against corrosion. If the thickness is high, the cost will significantly rise with minimal advantage.
The gold layer that ranges between 0.05 and 0.1 micrometers protects the nickel against oxidation while keeping it cost-effective. However, going beyond 0.125 micrometers can lead to a risk of corrosion since the high gold could cause variations.
Ensuring Compliance in PCB Manufacturing
Attaining ENIG compatibility with IPC is not possible without effective processes, qualified staff, and quality controls:
Enforce Tight Controls on Processes: It is essential that the parameters involved in the plating process, such as the chemical composition of the solution, temperature, and immersion time for the substrate in the solution, be strictly controlled. Such automation allows for constant monitoring.
Perform Routine Tests: Non-destructive testing procedures, such as XRF, evaluate the thickness of each layer, thereby confirming IPC-4552 specifications. Other solderability and corrosion-resistent tests verify the quality of the finish.
Educate and Train Personnel: Provide assurance that persons participating in the ENIG plating process have been adequately trained on IPC requirements, standards, and practices with the capability to address deficiencies in plating, including black pad disease.
Partner with Reliable Suppliers: Partner with dependable suppliers for the chemicals and materials used for surface finishing. Use of low-quality materials will undermine the compliant ENIG process since poor-quality material may require costly rework or prove nonfunctional.
Keep Informed About Revisions: The IPC standards are updated from time to time based on emerging challenges in the electronics assembly field. Staying ahead of updates, such as that of the IPC 4552B, allows processes to comply with the latest guidelines.
Advantages Of Compliance With ENIG IPC Standards
Observing standards of ENIG IPC prevents a wide array of issues and provides several benefits to manufacturers as well as users:
Improved Reliability: ENIG compliant PCBs are less likely to experience failure, even in stringent applications such as automotive and medical applications.
Improved Solderability: Correct ENIG process handling can ensure sound solderability, thus eliminating the possibilities of errors during the assembly process.
Cost Efficiency: The prevention of defects and rework ensures that manufacturers reduce production costs and offer prices that are very competitive.
Customer Trust: By adhering to standards like IPC-4552, it ensures customer trust, which is quite essential in the field of engineering.
Overcoming Challenges in IPC Compliance
Some of the issues that may arise in following the IPC standards are:
Nickel Corrosion (Black Pad): Improved by enhancing the Immersion Gold Process to reduce porosity.
Thickness Variability: Computerized technology guarantees precise plating.
Lead-Free Soldering Adaptability: Finishes are tested for stability in lead-free soldering.
For a very competitive industry such as PCB manufacturing, compliance with standards such as ENIG IPC-4552 is a necessity for ensuring quality, reliability, and customer satisfaction. With a focus on quality plating, thickness requirements, and effective compliance, manufacturers can make ENIG finished PCBs that are at their best as far as performance and durability are concerned, irrespective of whether they are manufacturing for consumer products or reliability segments.
PCBCart stands out for its complete PCB solution by strictly sticking to the highest quality standards, especially when it comes to ENIG surface finish. PCBCart is dedicated to being compliant with IPC standards to guarantee the production of products with the highest quality standards, and we have the best production infrastructure and staff to manufacture the best PCBs in the market. To make PCBs with the best market standards, get a free quote from our website.
Get an Instant Quote for High-Quality PCB Assembly
Helpful Resources
• Acceptance Criteria of IPC-A-600 in PCB Manufacturing
• How to Ensure the Quality of PCBs
• Reliability Comparison between Lead and Lead-Free Solder Joints
• PCB Surface Coating Functions and Selecting Principles
• Process Control Measures to Stop Defects in SMT Assembly














