As the core technology used in modern electronics manufacturing business, new materials, new technology and new equipment concerning SMT (Surface Mount Technology) assembly constantly emerge with assembly density going up, pin count rising and pitch down. Additionally, more SMDs (Surface Mount Devices) depend on visionless pins as package.
All the changes mentioned above bring forward higher requirement on inspections and tests applied in SMT assembly process and it’s increasingly more significant to set inspection and test procedures and pick up inspection technologies during SMT assembly.
SMT Inspection and Test Technology
During the process of SMT assembly, leading inspections and tests that are usually used include visual inspection, AOI (Automated Optical Inspection), X-ray inspection and ICT (In-circuit Test).
a. Visual Inspection
As far as its literal meaning goes, visual inspection refers to the inspection during which staff determine whether product quality conforms to manufacturing standard directly by observing target product with the help of naked eyes. Visual inspection has been widely applied due to its handy operation and low cost while its implementation is closely related with staff’s experience and work attitude. Plus, it fails to be used in the inspections on 0603 or 0402 packages and some fine-pitch components owing to physical limitations. Along SMT manufacturing line, visual inspections are usually applied after solder paste printing, before reflow soldering and after reflow soldering among which the visual inspection carried out prior to reflow soldering is of the most significance when it comes to SMT assembly quality guarantee.
b. AOI
Usually used just after post-reflow visual inspection, AOI test is applied to expose defects by the application of high-speed and high-accuracy optical process technology. As AOI machine is working, camera rapidly captures images of inspected targets and will compare them with proper parameters that have been restored in the database so that PCB (Printed Circuit Board) defects will be found out and automatically marked through monitor.
The advantages of AOI equipment include easy-to-learn programming and simple operations. However, AOI fails to be used on structural inspections of components with solder joints that are visionless, BGA (Ball Grid Array) for example. In addition, AOI also fails to display the unobvious defects such as component and PCB warpage.
c. ICT
Devices for the implementation of ICT include flying probe tester and bed of nails tester and test targets are usually modules going through SMT assembly. Electrical performance of components on PCB can be tested by ICT and the defects include missing parts, wrong parts, defective components, shorts, opens and defective assembly etc.
d. X-ray Inspection
X-ray inspection is used to inspect solder joint quality through scanning on PCB. Soldering quality can be clearly reflected thanks to the penetration of x rays. Compared with AOI, X-ray inspection is more capable of displaying more dimensions of solder joints but features higher cost.
The inspections introduced above feature their own attributes and they should be appropriately picked up in accordance with the specific targets to be inspected during SMT assembly. The comprehensive application of multiple inspection methods is helpful in reducing rework cost and improving percent of pass.
SMT Inspection Placement Settings
Inspections mainly take place in the following steps during the whole SMT assembly procedure from raw material acceptance to assembly completion.
a. Incoming Inspection before Assembly
The leading mission of incoming inspection aims to carry out quality monitor on all materials taking part in SMT assembly, including PCB bare boards, stencil, components, solder paste etc.
b. Process Inspection during SMT Assembly
Process inspection during SMT assembly is used to test the performance, analyze and deal with defects, including solder paste printing, chip mounting and reflow soldering.
c. Module Inspection and Rework after Reflow Soldering
Assembly quality and function of assembled modules is inspected after reflow soldering and rework measures can be made in time to overcome defects.
Incoming Inspection
Incoming inspection is usually implemented by naked eyes, that is, visual inspection, and its inspection targets include PCB bare boards, components and solder paste.
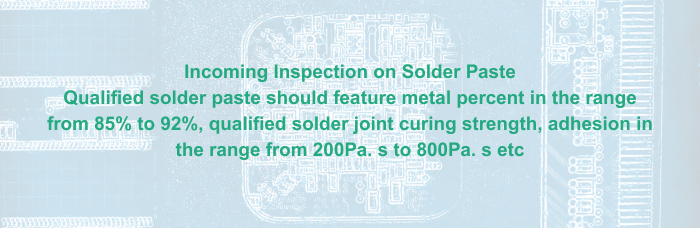
a. Incoming Inspection on PCB Bare Board
Size and Appearance Inspection
Bare board size inspection items include aspect ratio, space and tolerance, and PCB edge size. Its appearance can be inspected by PCB inspector with inspection targets featuring interior/exterior layers of multi-layer PCB, single/double-sided PCB and inspection items opens, shorts, scrapes, line width, tracing and other defects.
Warpage Inspection
The manual measurement method on PCB warpage is to measure the distance from the fourth corner to table surface while tightly pressing the other corners of the board to table surface.
Solderability Inspection
The focus of SMT solderability inspection lies in pad and electroplated through hole inspection, including edge edge dip test, rotation dip test, wave dip test and solder ball test.
Internal Defect Inspection
Microsection technology is usually applied for PCB internal defect inspection with inspection items covering thickness of copper with tin-lead alloy, alignment between conductive layers, lamination etc.
b. Incoming Inspection on Components
First, incoming inspections should be made on components in accordance with corresponding standard and regulation. Items concerning components inspection include the following aspects: whether component performance, specification and package conform to order requirement, to product reliability requirement, to assembly technology and assembly equipment requirement, to storage requirement. Apart from the above general inspections, lead coplanarity, lead coating layer thickness should be inspected to ensure they are compatible with technology requirement and capable of standing 10-cycle heating.
c. Incoming Inspection on Solder Paste
Qualified solder paste should feature metal percent in the range from 85% to 92%, qualified solder joint curing strength, adhesion in the range from 200Pa. s to 800Pa. s etc.
In-Process Inspection
SMT assembly manufacturing mainly covers the following procedures: solder paste printing, chip mounting and reflow soldering. To improve percent of pass, inspections have to be made during the whole process of SMT assembly manufacturing. As a result, quality control has to be made after each significant procedure so that defects occurring in the last procedure can be exposed in time with unqualified products entering the next link.
a. Solder Paste Printing Inspection
Solder paste printing inspection standards include the following aspects:
•Solder paste should be evenly printed;
•Solder paste image should align with pad in both size and shape;
•Solder paste amount and thickness should be compatible with requirement;
•Solder paste should be molded with no collapse or cracks;
•The pad area covered by solder paste should be compatible with standard.
b. Chip Mounting Inspection
Chip mounting defects include misplacement, parts missing, excessive glue, parts error, wrong direction, floating and rotation. As soon as the above defects take place, corresponding parameters should be modified in time to obtain ideal chip mounting result.
c. Reflow Soldering Inspection
Soldering defects that frequently take place include tombstone, insufficient solder, oxidation, void soldering, solder balls, cold soldering etc. Tombstone refers to the phenomenon that components stand after soldering; insufficient solder refers to the phenomenon that solder paste thickness is less than a quarter of component thickness; oxidation refers to the phenomenon that the shape of solder paste is irregular; void soldering refers to the phenomenon that there’s no solder paste between component and pad; solder balls refer to tiny or irregular-shaped soldering balls formed by melting solder in the process of reflow soldering; cold soldering refers to the phenomenon that reliable IMC isn’t generated between soldering surface and pad and once external force is used, components will possibly become loose.
Product Inspection and Rework
a. Product Inspection
After SMT assembly manufacturing is completed, qualified product will enter the next test link: ICT and function test.
Up to now, commonly-used ICT equipment is flying probe tester that depends on probes to replace nail fixture on bed of nails tester. Test is implemented by high-speed moving probes and test procedure can be directly captured through CAD software. While the flying probe tester is working, electrical connection between components and board is tested based on coordinate positions with specific positions marked so that all kinds of invisible defects can be accurately found out.
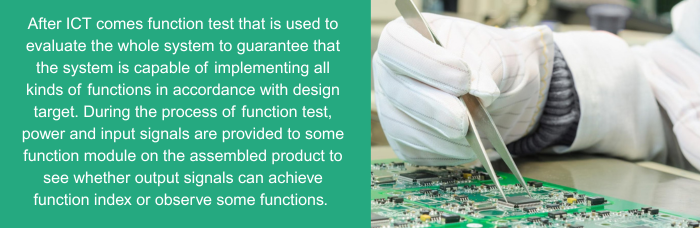
After ICT comes function test that is used to evaluate the whole system to guarantee that the system is capable of implementing all kinds of functions in accordance with design target. During the process of function test, power and input signals are provided to some function module on the assembled product to see whether output signals can achieve function index or observe some functions.
b. Rework
Rework features two types when it comes to unqualified modules: manual rework and station rework. Manual rework calls for definitely high requirement on rework tools and operation level of rework staff. When it comes to rework on PCBs with high density of components such as QFP or BGA, professional rework station is usually used.
Chip Component Rework
Soldering defects of chip components usually cover tombstone, insufficient solder paste, shorts, displacement, cracks etc. Components suffering from tombstone defect should be taken out by electric soldering iron and then soldered back. Components suffering from insufficient solder paste should be overcome by supplementing solder paste by electric soldering iron. Components suffering from shorts should be divided by the application of electric soldering iron and from cracks should be replaced.
IC Component Rework
Soldering defects IC components hold usually cover bridging, lack of tin and displacement. Bridging can be overcome by electric soldering iron to get it divided; insufficient solder paste can be overcome by supplementing solder paste; IC components suffering from a high level of displacement should be taken out and get it soldered back in a manual method.
Electronics manufacturing has experienced significant expansion, particularly in the SMT assembly of electronics, which requires novel materials and techniques for mounting assembly densities and visionless pin issues. The application of robust inspection technologies like visual inspection, AOI, X-ray inspection, and ICT is paramount. These instruments provide essential monitoring during the SMT process, from initial material inspection to final product testing, to minimize defects and ensure product reliability is optimal.
PCBCart stands out through superior PCB SMT assembly ability founded on superior inspection methods that ensure superior quality and reliability. All our quality inspection procedures are properly designed to meet the demands of complex modern SMT assembly to ensure optimal performance. Excellence will be brought to every product through PCBCart.
Request Your Customized Quote for SMT Assembly
Helpful resources:
• Printed Circuit Boards Assembly (PCBA) Process - PCBCart
• PCB Manufacturing Process – A Step by Step Guide
• Advanced Turnkey PCB Assembly Service - Multiple Value-added Options
• PCB Design Tips to Better Take Advantage of PCBCart's Assembly Capabilities And Save Cost
• PCB Prototype Assembly Services

















