In the ever-evolving era of electronics, Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are the infrastructural support of almost every electronic device. Among various types of PCBs, polyimide PCBs have emerged as a favorite among both manufacturers and designers because they can be used in scenarios where flexibility, hardness, and resistance to heat are of prime importance. This article aims to provide an all-encompassing review of polyimide PCBs, their distinctive properties, their superiority over standard materials like FR-4, and their extensive applications in a wide range of industries.
What Are Polyimide PCBs?
Polyimide PCBs are a type of PCB whose base material is polyimide. Polyimide is one of the polymers that has a great level of heat resistance, mechanical strength, and chemical resistance. Such properties make it best suited to be used for flex and flex-rigid PCBs. Polyimide makes the board twist and bend relative to other rigid PCB materials, but in a manner that will make the board flexible enough without compromising the board's performance integrity.
Polyimide vs. FR-4 Materials
When selecting materials for PCB production, what the end product will do and where it will be used typically dictates material choice. Here is where the significant differences between polyimide and most common FR-4 emerge.
FR-4 Material: FR-4, a composite woven fiberglass and epoxy resin with flame retarder, represents the industry standard for most applications. It provides a uniform blend of good mechanical toughness, insulation, and moisture resistance. However, it is brittle, and hence it shall not be employed in applications where there is a need for flexibility or thermal resistance at high temperatures. FR-4 degrades under high conditions and is not designed for ultra-high temperatures, the glass transition temperature being attained quite quickly.
Polyimide Material: Polyimide PCBs, on the other hand, are greatly sought after due to their reliability of performance up to 260°C or even higher, depending on the type of material. The flexibility of polyimide PCBs also makes them ideal for applications where the PCB has to fit into odd shapes or is subjected to mechanical stress, such as in aerospace, automotive, and high-cost consumer electronics.
Types of Polyimide PCBs
The versatility of polyimide as a material for PCB is seen with different types available, each suitable for different applications:
Pure Polyimides: Due to their simplicity and inherent stability, pure polyimides do not contain other fire retardants, and this means they have improved thermal stability and flexibility. They are best suited for application where heat performance is critical.
Third Generation Polyimides: They contain flame retardants for enhanced fire resistance. Compromising on slightly less thermal stability compared to pure polyimides, they offer a cost-effective means of large-scale production as they require less curing temperatures.
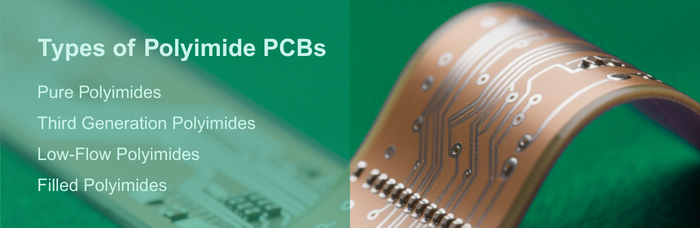
Low-Flow Polyimides: Reduced flexibility of these makes them more compatible with static uses under harsh conditions. Their resistance to heat and warping is very high, and hence they are best utilized in aerospace and military applications.
Filled Polyimides: These are filled with fillers that reduce the resin shrinkage when curing, possessing an extremely long lifespan and resistance to expansion and contraction stresses. They are less brittle and stronger compared to traditional rigid boards.
Advantages of Polyimide PCBs
Therefore, polyimide PCBs possess several distinct advantages:
Durability and Flexibility: Unlike hard FR-4 boards that crack when subjected to mechanical stress, polyimide PCBs are bendable multiple times and can resist vibrations, making them priceless in use for dynamic mechanical motions like wearable technology and auto components.
Thermal Stability: Being able to handle colossal heat, polyimides escape thermal damage that occurs in high-temperature applications, thus ensuring reliability even in maintenance.
Chemical Resistance: Their superior chemical and solvent resistance prevents them from eroding and other chemical damage, enabling longer use time on the PCB and mounted components.
Tensile Strength: With greater elasticity, polyimide PCBs are able to support more mechanical loads, a valuable characteristic where the application of structural support is needed.
Design Flexibility: Polyimides enable engineers to design PCBs for accommodation into unusual spaces, a requirement for miniaturized consumer goods and emerging wearables technology.
Applications of Polyimide PCBs
Polyimide PCB's flexibility and durability ensure their application in numerous high-risk sectors:
Military Use: Polyimide PCBs are optimally suited for military systems that demand uncompromising operational integrity and reliability at extreme temperatures. They find application in microwave processing, navigation, and power distribution systems.
Aerospace Industry: In aerospace, where high-temperature performance, light weight, and reliability are top priorities, polyimide PCBs are used in satellites, engine control units, and flight sensors.
Medical Devices: Medical devices require PCBs with high levels of quality and endurance. Polyimide PCBs are used in medical equipment such as MRI machines, ultrasound machines, and wearable health monitoring systems, where they perform impeccably even when subjected to chemicals and repeated usage.
Commercial Electronics: With consumer electronics growing more sophisticated, miniaturized, polyimide PCBs are on greater demand. They allow for the functionality of smartwatches, gaming systems, and high-definition TVs with enhanced performance and the potential to be used in svelte designs.
Telecommunications: With global connectivity more critical than ever, polyimide PCBs are part of the success and maintenance of effective and reliable operations in cell towers and communications equipment that are key elements of modern telecommunications infrastructure.
Polyimide PCBs leverage their unique material attributes to provide beyond-product solutions compared to traditional PCB materials like FR-4. Their toughness, thermal stability, and roughness make them key in applications where companies require next-generation electronic solutions to withstand tough conditions. As technology advances, polyimide PCBs will increasingly be a necessity to push the boundaries in electronic design and functionality.
At PCBCart, we work to offer high-performance polyimide PCBs with specifications tailored to the specific needs of each of our clients, guaranteeing unparalleled performance and reliability for every project. Whether for medical, or commercial use, our PCB manufacturing expertise offers the capability to make your most demanding electronic designs a reality with precision and excellence.
Request for Advanced PCB Manufacturing Quote at PCBCart Now
Helpful resources:
• Flexible PCB Fabrication Technology Development
• Applications and Types of PCBs for Military and Defense Industry
• PCB Material Selection Based on Electrical Performance and Cost
• PCB Thermal Design Considerations
• High-Tg PCB