Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) design is an important step in the process of creating electronic equipment. Accuracy in the specification of PCB sizes is significant in that it not only determines the physical dimension fit in the device enclosure but also the functionality, manufacturability, and cost of the final product. The guide will take you through necessary steps to develop PCB size, provide insight into efficient planning of the layout, component positioning techniques, and workable manufacturing provisions.
The Significance of PCB Dimensions
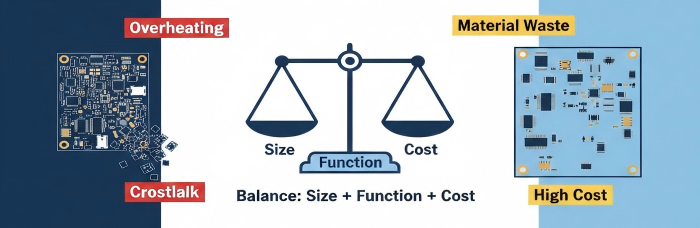
The selection of the appropriate PCB size is essential for several reasons. A small PCB may cause lack of enough space to fit the components and consequently cause overheating or crosstalk. On the other side, PCB waste materials are over sized and add to expenditure. In this manner, it is important to find a balance between size, functionality, and cost. The proper design is critical in terms of dimension planning because it will not only make the design functional but also manufacturable and cost-effective.
Step 1: Component Footprints and Sizes
A PCB design is based upon a detailed knowledge of the components used:
Component Footprints: Start with a list of components required in your project. Record correctly the size of every part, pads, pins and clearances needed to solder and transfer heat. Use design software but one which offers libraries of standard footprints, but it is always necessary to check against official datasheets to ensure that there are no differences.
Maximum Height Take into Account: Other components are height limited by enclosures, which must be taken into account to ensure that they do not interfere.
Step 2: Component Spacing Requirements
Spacing of components is essential to a successful assembly as well as successful operation:
Surface-Mount Devices (SMDs): Be sure that there is a minimum of 0.2 mm to 0.5 mm space between devices to ensure that the soldering process is accurate and short circulating is avoided.
Through-Hole Components: Have 1 mm to 2 mm of clearance to minimize the mechanical stress during assembly.
High Voltage Areas: The high-voltage components need extra spacing to avoid arcing, based on standards like IPC-2221.
Heat-Sensitive Components: Power components, such as transistors, need to be separated by at least 3 mm of other components to allow sufficient heat dissipation.
Step 3: Trace, Via, and Other Features Planning
Once accommodation components are done, take into account other board characteristics:
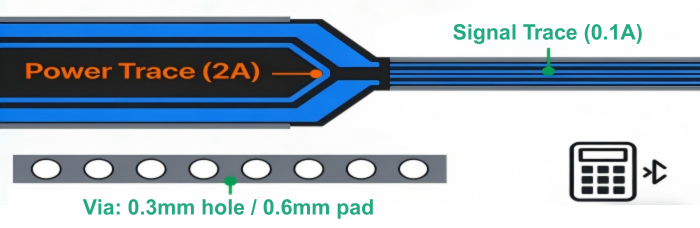
Trace Widths: Trace width calculators should be able to take into account the current and temperature rise in order to decide on trace widths. Balance between carrying capacity and space is important, particularly when low-power signals might need very small widths, whilst power signals might need very large traces.
Vias and Holes: Vias are usually of a diameter of 0.3 mm with 0.6 mm diameter pads. Via space needs to be taken into account during routing strategy, and edges are to be spaced 2 to 3 mm apart.
Step 4: PCB Design Software for Layout Simulation
The software PCB design cannot be done without visualizing and optimizing your layout:
Layout to Schematic Transition: Use your schematic design, which must be an accurate description of the circuit. Then drag this to the layout editor.
Place Component: Critical components should be strategically placed such as connectors and power ICs. Layout components in a rational way so as to reduce trace length and boost functionality.
Design Rule Check (DRC): Design software. Design rule checks are used to automatically verify that the layout meets all required spacing and clearance requirements, and verifies when the layout is violating those requirements.
Step 5: Enclosure and Mechanical Constraints
The size of your PCB should fit into the size of its enclosure:
Fit Check: Fit the board in its desired housing. Consider dimensions as well as mounting characteristics and connector protrusions.
Mechanical Stress: Place heavy or delicate parts in the middle of board in case of vibration, or bending, to eliminate detachment or damages.
Step 6: Managing and Cost Optimizing
Manufacturability A design that has manufacturability in mind can be much less expensive to produce:
Standard Panel Sizes: Use standard panel sizes (usually 18 x 24 inches) in order to reduce waste. Layout your PCB design so that you can use these panels to their fullest extent.
Production Guidelines: Minimum and maximum size should be followed based on instructions given by manufacturers. This encompasses trace widths, hole sizes, and the general board sizes.
Case of PCB Dimension Calculation
Consider that you are to design a PCB of a small IoT device. It is a board that consists of a microcontroller of 10 mm x 10 mm footprint, two 5 mm x 5 mm sensors, and various other small passive components. The first arrangement may involve having the microcontroller at the centre, and the sensors and passives surround it. This design (where there is sufficient spacing and trace routing) may initially provide a rough dimension of 29 mm x 24 mm. This should be simulated into design software to guarantee that all the rules are followed before completion.
The ability to master the science of PCB size determination is a key to the success of any electronic product. Designers can make sure that their PCBs are both operational and cost-effective by ensuring that they have a good comprehension of component footprints, that they meet strict spacing constraints, that they take appropriate advantage of layout simulation software, and that they are manufacturing-friendly. This guide will give you the steps and considerations to make to create well-sized, reliable boards that will fit the technical requirements of your project and still fit within the budget constraint. This leads to a seamless flow between design and production, reducing expensive redesign and delivery of the product on time.
PCBCart is one of the leading suppliers when it comes to high-quality PCB manufacturing and assembly. Our multi-layer fabrication, meticulous quality control and customizable options add to a broad assortment of our services, which means that our design specifications are fulfilled accurately. We have experience in dealing with various projects, including simple designs to intricate high-density PCBs, which enable us to handle any challenge efficiently and excellently. Quote PCBCart today and see the difference that our promise of quality and customer satisfaction can provide you with.
Request for Advanced Assembly Solutions Now















