Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are essentially the backbone of modern electronics. The solder mask is a very important component in the PCB manufacturing process, which protects against oxidation, reduces solder bridges, and increases the visual appeal of the PCB. The quality of the solder mask is essential for the dependability and functionality of a PCB. This tutorial aims to provide information regarding the testing of solder mask quality along with the selection and solderability test of solder masks.
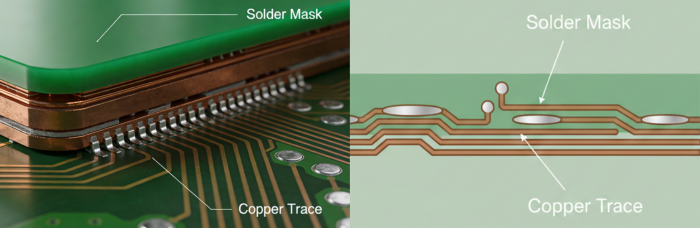
Understanding Solder Masks
Solder masks, sometimes referred to as solder stop masks, are layers of polymer applied to cover the copper traces on a PCB. They perform several critical functions:
Prevention of Solder Bridges: Solder masks prevent short circuiting by creating insulation between conductive traces.
Protection against Oxidation: The paint serves as a protective barrier against the environment, thus protecting against oxidation.
Aesthetic Enhancement: The pigmented layer is responsible for making PCBs appear as they do and can also be made in different colors as desired.
Whether to use liquid epoxy solder mask, photoimageable solder mask, or solder mask using a dry film depends on the complexity of the PC boards as well as budget constraints. For example, photoimageable solder masks exhibit high precision, which makes them ideal for complex designs, while a dry film has a constant thickness ideal for flat PC boards.
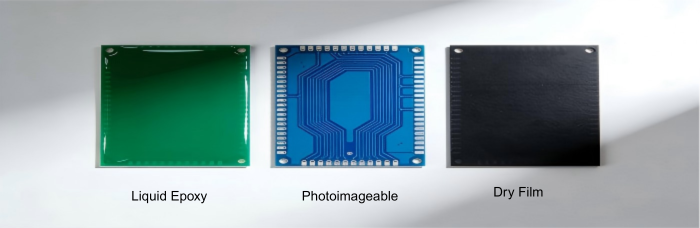
Selecting the Correct Solder Mask Material
There are various considerations in arriving at the type of the solder mask to be used in the board:
Board Complexity: Complex component placement patterns can be effectively tackled by the use of LPSM, which enables high accuracy in accordance with complex topology requirements.
Surface Flatness: DFSM is perfect for boards with planer surfaces because it provides an equal thickness of the mask.
Manufacturing Constraints: The solder mask type has to complement the manufacturing processes available within the fabrication facility.
Proper selection guarantees maximum security within both production and functioning stages.
Solder Mask Inspections
Examination of the solder mask is an important process during quality, which ensures that the solder mask satisfies the standards before the board goes for the assembly process.
Visual Inspection
Color and Uniformity: Uniformity without any patches on the board defines the correct implementation of the solder mask. Discrepancies may indicate problems during the thermal or mechanical processing steps.
Coverage and Alignment: Verify the masks for proper coverage of the intended area and proper alignment with the design pattern, particularly around the pads and vias.
Adhesion Testing
Cross-Cut Test: In this test, the surface of the mask is scored to create a grid pattern, tape is applied, which is then peeled off. This determines which part of the mask is peeled off to check adhesion strength.
Thickness Measurement
Gauging Tools: Use non-contact thickness gauging tools in order to provide the solder mask with a thickness of between 0.3 and 0.8 mils. This is essential to ensure optimal functionality.
Solderability Testing
Solderability testing looks at the condition of the PCB to determine whether it can form a proper solder joint that will ultimately retain the components in place throughout the assembly process.
Dip and Look: Components are dipped in solder post accelerated aging to confirm wetting due to activated rosin flux under long-term exposure conditions.
Surface Mount Simulation: This test is designed for SMT components using specific solder paste with a convection profile to see the adherence of the components while in reflow.
Wetting Balance Test: This test quantifies the solderability of finishes by measuring the wetting forces over time.
These processes assure the reliability of solder connections on the PCB against possible failures due to poor wetting or attachment.

Solder Mask Defects Troubleshooting
Finding and fixing solder mask defects is an essential process in ensuring PCB quality. Some common solder mask defects include cracks, peeling, misalignment, and lack of coverage. If any of these problems occur, the following procedures can be used in fixing them:
Cracking or Peeling Repair
Repair Process: Apply UV-curable solder mask material on the areas needing repair. Use a UV lamp for curing, ensuring that copper traces left exposed will no longer be vulnerable to corrosion.
Handling Incomplete Coverage
Additional Mask Application: Additional solder mask needs to be applied to the affected region by precision tools.
Misalignment Correction
Manual Correction: Additional solder mask can be applied for manual correction when there are slight misalignments. For greater discrepancies, joint efforts with manufacturers can make changes to design files going forward.
Avoidative Methods
Preventing solder mask defects rather than solving them after they occur is always preferable. Just some of the methods for this are as follows:
Design Optimization: It is important for the needs of the solder mask, for example, via tenting and pad clearance, to be clearly spelled out in the design files.
Material Choice: Use good-quality solder masks that can protect against natural and operational stresses.
Controlled Manufacturing: The environment during manufacturing can be controlled for optimal curing temperature (usually 120-150°C) to avoid defects such as blister formation.
The solder mask is much more than a protective agent but rather an integral part of the functionality and durability of the board. Ensuring solder mask quality is one of the critical sides of PCB manufacturing. Board manufacturers can improve performance reliability by choosing appropriate types, performing detailed inspections, and rigorous testing protocols, respectively. Taking a preventive approach minimizes defects, reworks, and associated costs while maintaining electronic product integrity and efficiency in the market.
PCBCart excels at PCB manufacturing and assembly, and our expertise and quality for every project undertaken cannot be matched. Our commitment is that every solder mask on our PCBs will be applied accurately and inspected thoroughly by our state-of-the-art technology team. At PCBCart, we realize that quality is crucial for every detail, including solder masks, and we have specialized services that cater to different sectors for different levels of complexity in PCB designs. Get a quote at PCBCart today and enjoy top-notch quality for your project!
Start a Free and Fast Quote for Advanced PCB Assembly
Helpful Resources
• The Most Comprehensive Guidelines for Surface Finish Selection
• How to Ensure the Quality of PCBs
• Process Control Measures to Stop Defects in SMT Assembly
• Contrast on Soldering Technologies Used in Lead and Lead-Free Reflow Soldering
• PCB Surface Coating Functions and Selecting Principles















