In the fast-paced electronics industry, the complexity involved in multi-layer PCB design is what is needed to make the methods reliable and effective when it comes to the performance and durability of the current gadgets. The layer stackup, which is a major component of this design process, is critical in electromagnetic interference (EMI) management. Although a well-considered PCB stackup can help in improving EMI performance as well as in signal integrity, a poorly implemented stackup can greatly impair it. This paper will examine the complex connection between the layer stackup and EMI performance, and present solutions to the task of optimizing your PCB designs to achieve a better EMI performance.
The Complexity of PCB Layer Stackup
In a multi-layer stackup, different layers of conductive and insulating material are stacked up and these include: signal layers, ground planes, and power planes. This design is selected on the electrical, mechanical and thermal requirements of the application. Typical stackup designs are 4-layer, 6-layer and 8-layer boards although stackup diminishes in complexity as higher speed and density applications are required.
The stackup has a strong effect on signal paths, power allocation and shielding of the board against undesirable electromagnetic signal interactions. Without proper design of the stackup, crosstalk, signal integrity issues and inability to comply with regulatory EMI can occur. To attain effective EMI shielding and reliability of your product in the real-life scenario, it is crucial to optimize your multi-layer PCB stackup.
The influence of Layer Stackup on EMI Performance
A number of important elements in the stackup make it affect the performance of EMI. The insight into them can help to mitigate the vulnerability to EMI and guarantee the adherence to EMC norms.
Proximity of Ground Planes
Ground planes can be used as a reference point of signals and they give shielding to the EMI. Having signal layers near to a ground plane reduces the return path of the high-frequency signal and this lowers loop area and radiated signals. A standard 4-layer stackup would have signal layers placed next to ground planes thereby essentially reducing the impedance and also increasing EMI control.

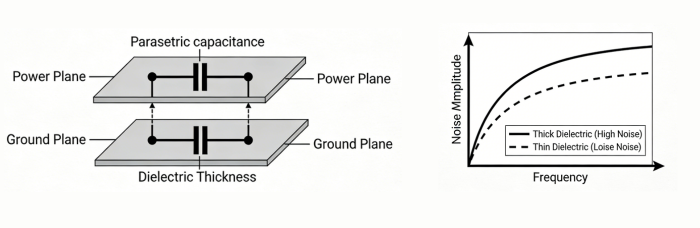
Coupling between Power and Ground Planes
The natural capacitive layer formed by proximity between the power and ground planes is vital in decoupling the high frequency noise. The use of this strategy can provide a board with stability in the voltage and reduction of noise, offering it a low-impedance pathway of return currents. With a 6-layer stackup, when power and ground planes are placed in the intermediate layers, it improves noise reduction and EMI performance.
Stackup Symmetry
Not only does a symmetrical stackup have importance in terms of structural integrity, but also in terms of uniform EMI performance. Equal signal, power and ground layers contribute to the preservation of consistent impedance, as well as the reduction of EMI. As an example, an 8-layer stackup characterized by signal and ground layers alternating means that every signal layer will enjoy the advantages of grounding in one directly adjacent layer, leading to ideal shielding of EMI.
Optimization Strategies to Stackup for EMI Performance
Having knowledge of the effects of stackup on EMI, designers are able to use effective methods in reducing interference and in improving performance.
Prioritize Close Signal-Ground Placement
In high-speed signals, have position ground planes adjacent to signal layers in order to reduce inductance and isolate electromagnetic fields. Between these conducts, much smaller dielectric layers may radically reduce radiated EMI, with a controlled impedance often in the range of 50 ohms.
Exclusive Power and Ground Planes
Dedicated ground and power planes are necessary to achieve good EMI reduction. Split planes need not be split when unnecessary because this may cause EMI hotspots. Add decoupling capacitors around the power pins of the ICs in order to reduce noise.
Optimize Layer Spacing
Reduced distance between power and ground planes increases capacitance which suppresses noise. Use impedance calculators to find the best dielectric thickness to use in high-speed designs.
Minimize Signal Layer Crossings
Use fewer vias to ensure continuity of the return path and minimize EMI. In case it is impossible to avoid, locate stitching vias attached to ground close to signal vias to ensure a small loop area.
Shield Sensitive Signals
Placing delicate analog or RF signals between ground planes provides a Faraday cage effect, which improves the protection against external interference.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Even with well-intended stackup design, some of the errors may affect the EMI performance. Fragmented ground planes should be avoided thus disturbing return paths and the placement of the power planes should be appropriate in order to provide a close distance to the ground plane, which helps increase the decoupling effect. Also, watch out on loading signal layers to reduce crosstalk and EMI.
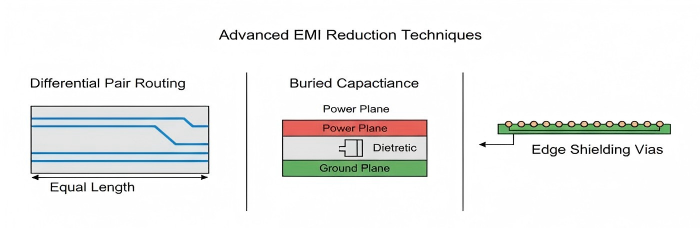
Advanced High-performance EMI Reduction Techniques
More sophisticated methods to reduce EMI in very complicated designs include buried capacitance, and differential pair routing. Use edge shielding on ground vias and pair routing always to keep noise off.
With the fast evolving electronics world, it is important to master the intricacies of the design of multi-layer PCB in order to guarantee the reliability and the performance of the contemporary devices. The layer stackup is a basic element of this design process and it is significant in the management of electromagnetic interference (EMI). Although a well-planned PCB stackup may improve EMI operation and guarantee signal integrity, a poorly implemented stackup may drastically worsen it. This paper discusses the complex interplay between layer stackup and EMI performance, and offers hints on how you can use all your PCB designs to achieve a better EMI performance.
To achieve high PCB solution which is effective in EMI management and all-round effectiveness, it is worth a partnering with PCBCart. PCBCart has years of experience and a desire to attain excellence, which is why we can provide the latest technologies in the fabrication industry and help you make certain that your designs are up to the standards of the industry. We understand the importance of the PCB stackup and runs personalized programs to make your designs work with EMI management. Get a quote with PCBCart and find out how we can make your innovative ideas come true with accuracy and dependability.
Get an Instant Quote for Advanced Multi-Layer PCB Assembly
Helpful Resources
• PCB Partitioning Design Rules for EMC Improvement
• Three Design Considerations Ensuring EMC of Laptop PCB
• High-Speed PCB Routing Techniques to Reduce the Influence of EMI
• Elements Affecting Characteristic Impedance of PCB and Solutions
• Problems of EMC Technology Application in PCB Design and the Strategies
• Antenna Design Considerations in IoT Design











